Retinol versus Vitamin C
Share
Which One Is Right for Your Skin?
If you’ve ever stood in front of the mirror wondering whether to reach for retinol or vitamin C, you’re not alone. Both ingredients are proven skincare powerhouses — but they do very different things.
Understanding how each one works can help you build a smarter routine and unlock your healthiest, most radiant skin yet.
In this guide, we’ll compare Retinol vs Vitamin C head-to-head: their benefits, differences, how to use them safely, and whether you can combine them for maximum glow.

Order Vitamin C and Retinol here
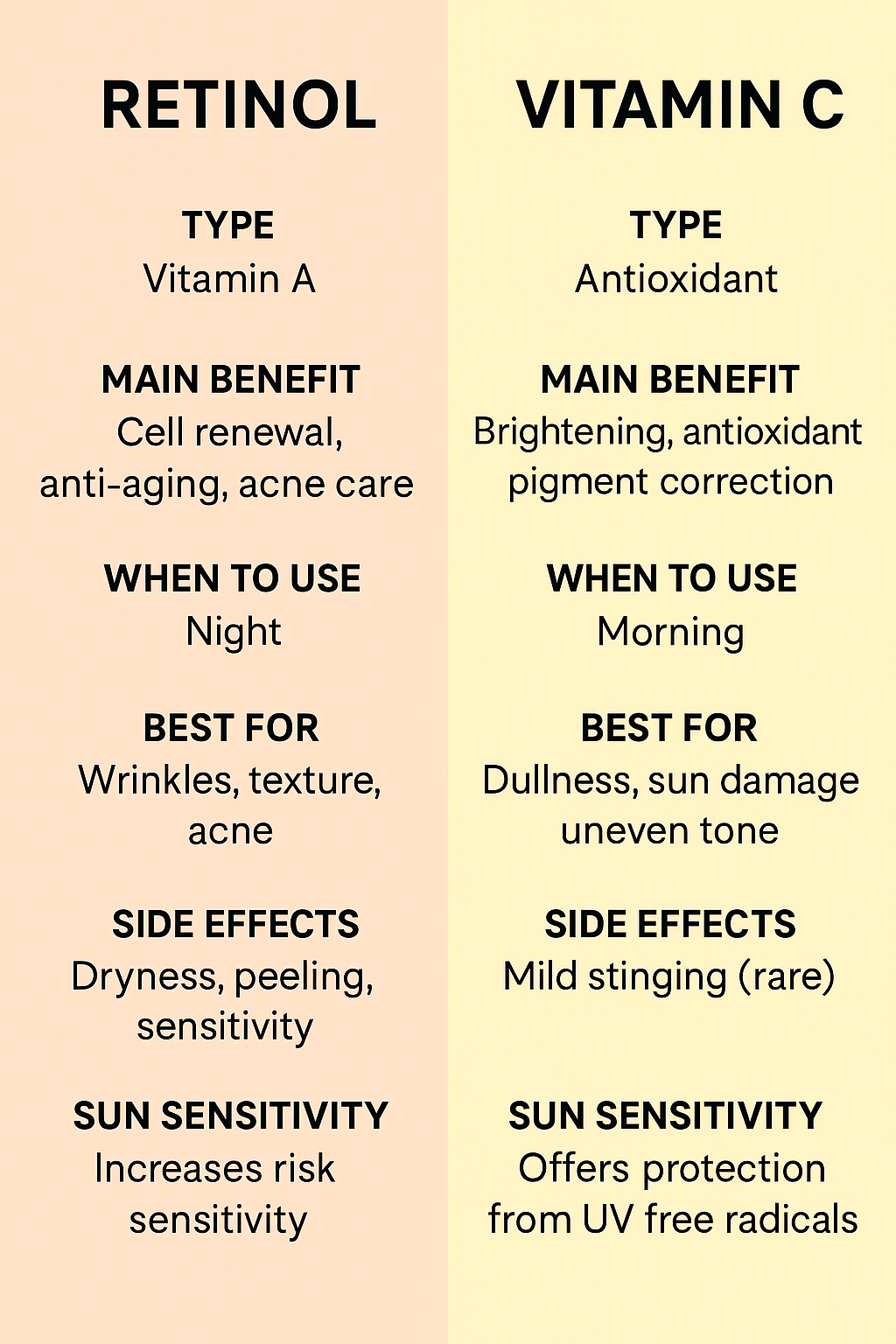
Retinol vs Vitamin C: Key Differences
Here’s how these two all-stars compare:
| Feature | Retinol | Vitamin C |
|---|---|---|
| Type | Vitamin A derivative | Vitamin C (antioxidant) |
| Main Benefit | Cell renewal, anti-ageing, acne care | Brightening, antioxidant, pigment correction |
| When to Use | Night | Morning |
| Best For | Wrinkles, texture, acne | Dullness, sun damage, uneven tone |
| Side Effects | Dryness, peeling, sensitivity | Mild stinging (rare) |
| Sun Sensitivity | Yes – increases UV sensitivity | No – offers protection from UV-free radicals |
In short:
- Retinol is the “resurfacer” — it renews the skin from within.
- Vitamin C is the “protector” — it shields skin from daily damage and keeps your tone bright and even.
Used correctly, they can complement each other beautifully.
Can You Use Retinol and Vitamin C Together?
This is one of the most common skincare questions — and the answer is yes, but with strategy.
Both are potent actives, but they work best in different environments:
- Retinol thrives in a neutral pH (less acidic)
- Vitamin C needs an acidic pH to penetrate properly
Layering them in the same routine can reduce effectiveness or cause irritation. The best approach is timing separation:
Option 1: Morning and Night Routine
- Morning: Cleanser → Vitamin C Serum → Moisturizer → Sunscreen
- Night: Cleanser → Retinol → Moisturizer
This is the safest and most effective way to enjoy the benefits of both.
Option 2: Alternate Nights
If your skin is sensitive, use Vitamin C one night and Retinol the next. This gives your skin time to recover while still providing consistent results.
How to Layer Them Safely
Here’s a dermatologist-approved approach:
- Start slow. Begin with low concentrations (0.25% retinol or 10% vitamin C).
- Patch test before full application.
- Introduce one product at a time. Let your skin adjust before combining.
- Use a moisturiser after both to buffer and hydrate.
- Sunscreen every morning — non-negotiable when using retinol.
- Avoid strong exfoliants (AHA, BHA, benzoyl peroxide) in the same routine.
Consistency is key. Expect visible improvement in 6–8 weeks for brightness, and 3–6 months for deeper texture or lines.
Which One Should You Use?
It depends on your skin goals:
- For wrinkles and texture: Go with Retinol
- For dark spots and dullness: Choose Vitamin C
- For acne-prone skin: Retinol helps unclog pores and reduce breakouts
- For environmental defence: Vitamin C strengthens antioxidant protection
- For ultimate results: Use both — Vitamin C in the morning, Retinol at night
If you’re new to actives or have sensitive skin, start with Vitamin C first, then gradually introduce Retinol once your barrier feels strong.
Retinol + Vitamin C Sample Routine
Morning Routine
Cleanser → Vitamin C Serum → Moisturizer → Broad-Spectrum SPF 30+
Evening Routine
Cleanser → Retinol Serum → Nourishing Moisturiser (with ceramides or hyaluronic acid)
For even more hydration, add a Hyaluronic Acid Serum before your moisturiser — this helps reduce potential dryness from retinol.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: Can I use retinol and vitamin C together?
Yes, but not at the same time. Use Vitamin C in the morning and Retinol at night for best results and minimal irritation.
Q2: Which is better for wrinkles — retinol or vitamin C?
Retinol is stronger for fine lines and texture because it directly stimulates cell turnover and collagen. Vitamin C supports collagen indirectly and protects against future damage.
Q3: Which is better for dark spots?
Vitamin C works best for brightening dark spots and improving overall radiance, while Retinol helps fade discolouration over time by renewing skin.
Q4: Can sensitive skin use both?
Yes — but introduce one active at a time, use gentle formulations, and moisturise generously.
Q5: Is retinol safe during pregnancy?
Most dermatologists recommend avoiding retinol during pregnancy and breastfeeding. Vitamin C, however, is generally considered safe — but always consult your doctor.
Final Thoughts: Retinol and Vitamin C Are Better Together
When used correctly, Retinol and Vitamin C form a powerhouse duo.
- Vitamin C shields your skin from daytime damage.
- Retinol renews and repairs while you sleep.
Together, they smooth, brighten, and protect — giving you a balanced, youthful complexion that glows from within.
Consistency, patience, and daily SPF are your secret weapons.
Pro Tip:
If you use serums, look for Hollyberry Cosmetics’ Retinol Serum and Vitamin C + Hyaluronic Acid Serum — formulated for maximum results with minimal irritation. Pair them with a hydrating moisturiser and sunscreen for complete care.
